Why do students come to yoga? Surface vs under-the-surface needs
3When students arrive in our yoga classes and private yoga sessions, they usually have a particular obvious reason for seeking our services. It often involves pain or limited mobility in some part of the body. My teacher Gary Kraftsow likes to say that pain is the greatest motivator; it propels us to take action. Going to a yoga class might end up being one of those actions.
Over the years of teaching, it became clear to me that in addition to obvious, surface needs that bring them to a class, our students also have under-the-surface needs, so to speak. A surface need is the one that the student can clearly articulate, like back pain, for example. Under-the-surface needs are the ones that they might not even realize themselves, yet they are there, they are important, and without acknowledging and meeting them we won’t make much progress toward resolving the surface needs.
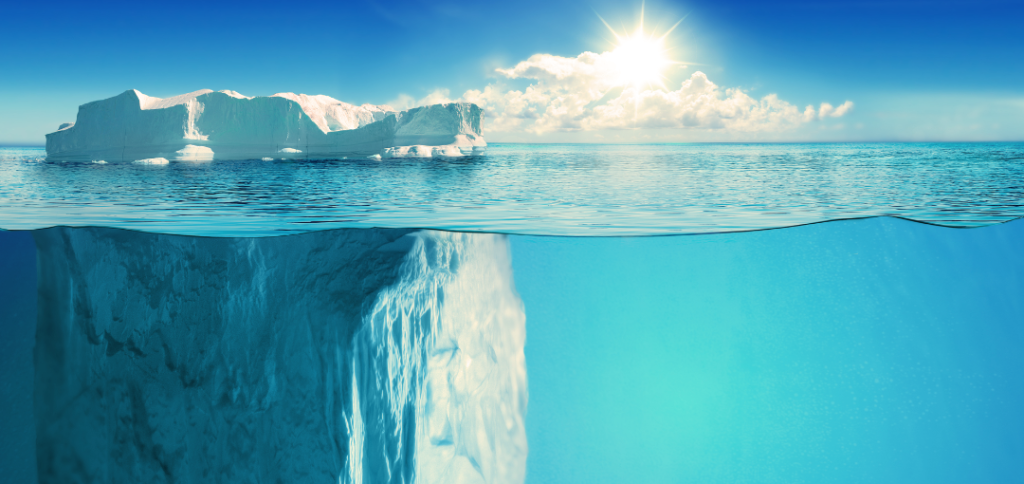

Here is a quick summary of the foundational under-the-surface needs:
First, every student needs to be heard, seen and acknowledged with compassion and curiosity. This means listening to the student without judgement or an agenda, asking relevant questions and tuning in to their body language and other visual cues. It also means staying open to whatever comes up and being willing go on a journey of exploration with the student in whichever direction that journey takes us. This is only possible when we, as yoga teachers, are self-aware and confident in our own knowledge. If we are too busy trying to control their experience or demonstrate our expertise to our students, we might miss or misinterpret the important clues they give us.
Second, most students need to change the way they view their condition or discomfort. After experiencing pain for extended period of time, that pain might become inseparable from the student’s perception of themselves. Encouraging them to look at it as part of their experience rather than the totality of it can help put it into prospective. One way to reframe their thinking is to encourage them to view each hurting part as a protector. Ultimately, our bodies do not like to be in pain. The pain might reflect the body part’s desire to protect the student and prevent further damage, or to bring attention to the area that needs to be cared for. Either way, looking at painful areas as protectors rather than troublemakers might help students feel more compassion and understanding toward those parts.
Third, every student needs to be empowered. The yoga tradition unequivocally states that each one of us has the inner essence, unchanging and compassionate Self that knows what’s best for us and knows how to heal our parts. In Sutra 1.2 yoga is defined as cessation of mental chatter. Once that mental chatter subsides, Sutra 1.3 continues, you can see your Self in its essence. Our job as yoga teachers is to help our students settle their mental chatter, encourage them to get in touch with their Self and give them support and relevant knowledge to attend to their surface needs. In practical terms, getting in touch with one’s Self manifests as becoming reflectively self-conscious about our experiences, actions and choices, having moments of peace and clarity about our situation, experiencing compassion for our own struggles, and having confidence in a positive outcome of our actions, including our yoga practice.
After we’ve acknowledged our student’s struggles, encouraged them to separate themselves from their suffering and helped them connect to their inner Self, only then we can address the surface symptoms and underlying reasons of their discomfort. This entire process requires clear communication and a lot of observation on our part. To be helpful, we need to understand what’s going on at different levels of our students’ systems. We can use a variety of tools to get that necessary information and we will talk about them next time – tune in!
[jetpack_subscription_form]








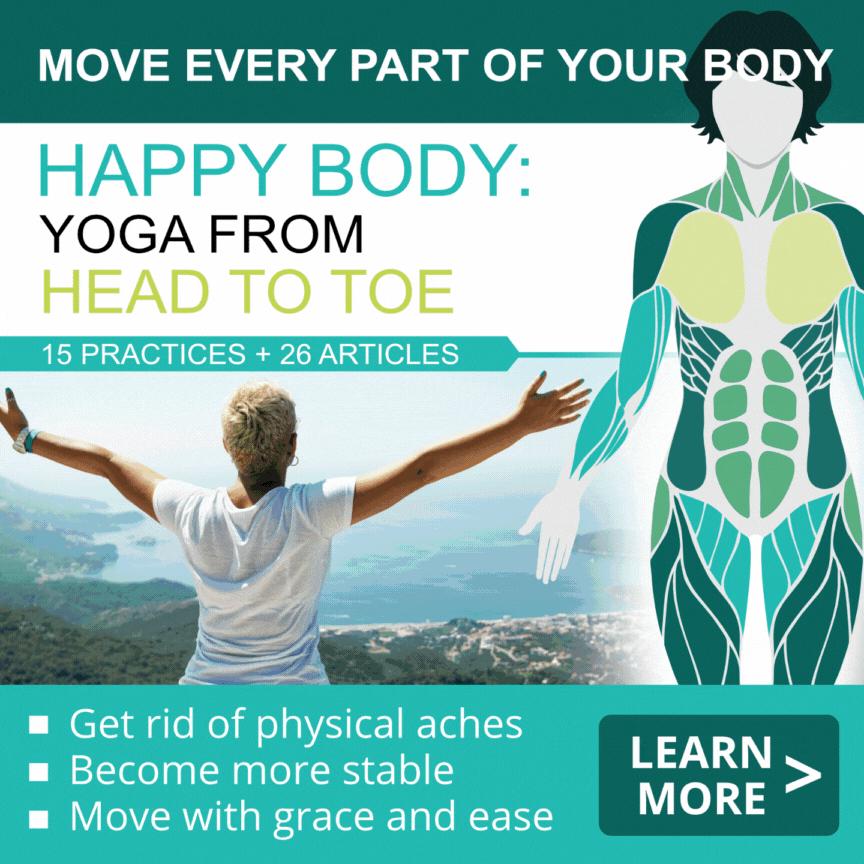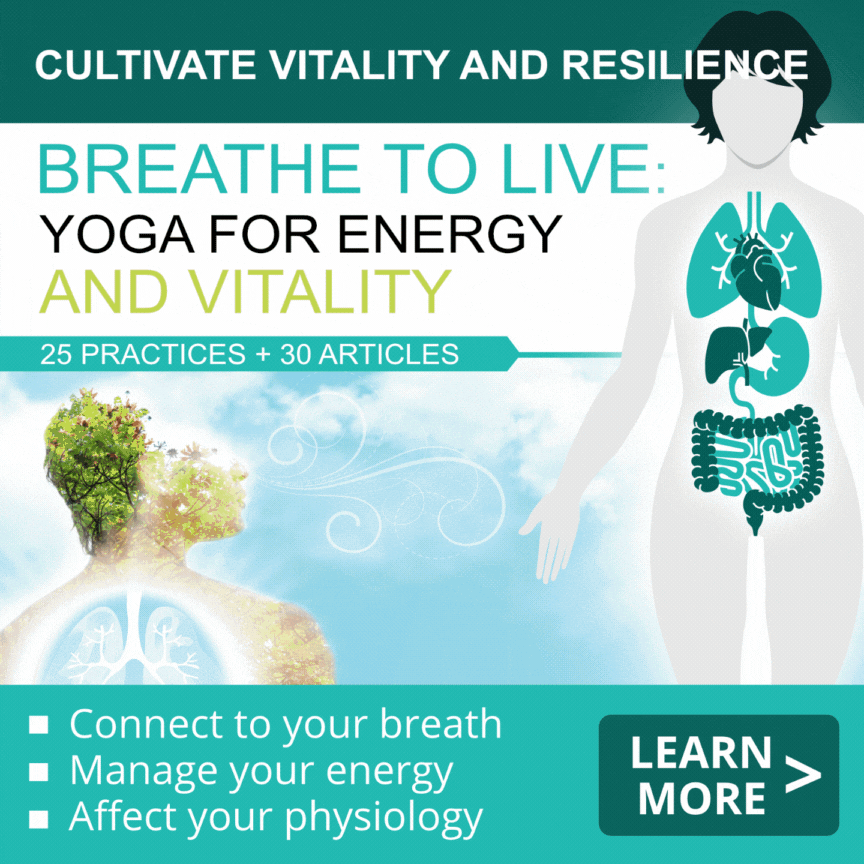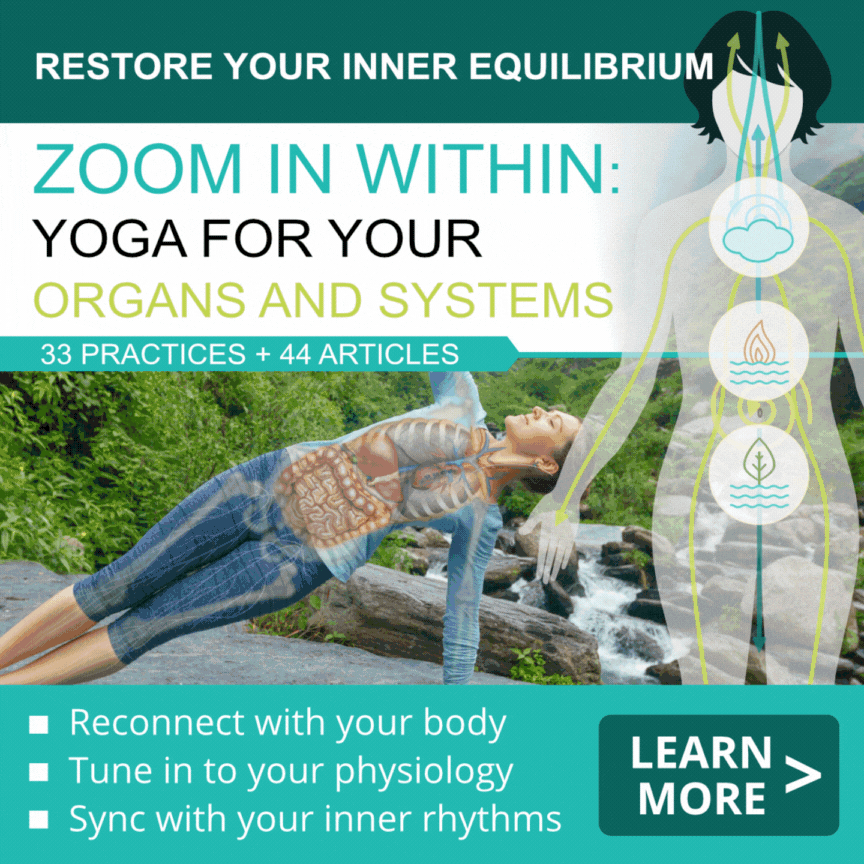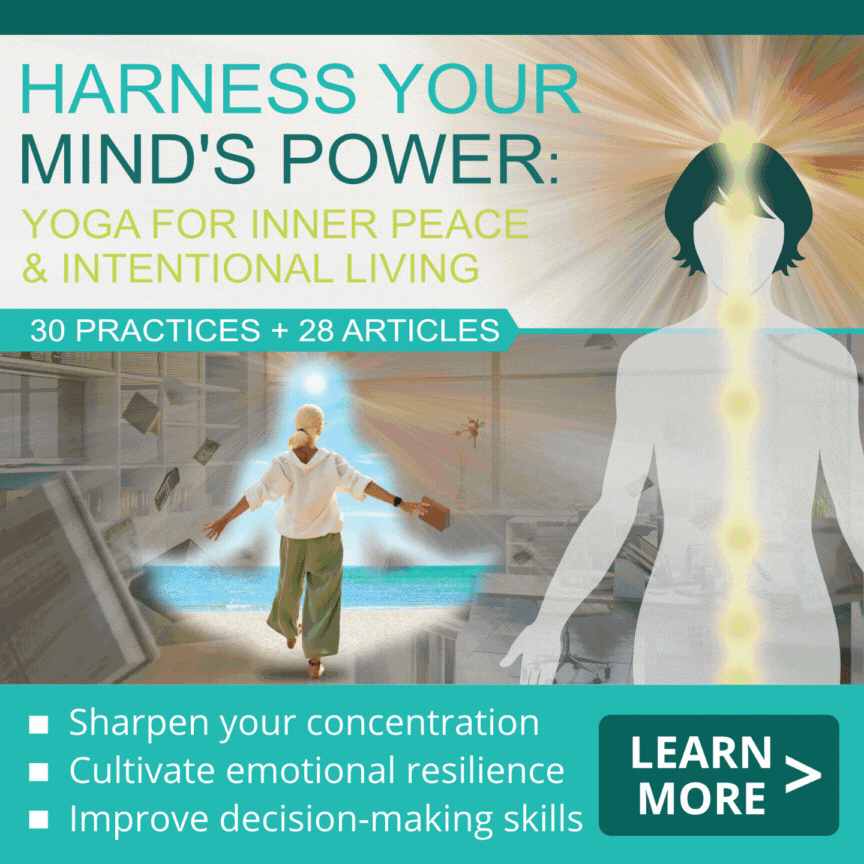








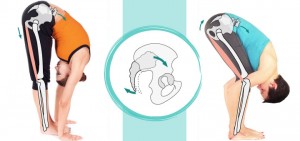
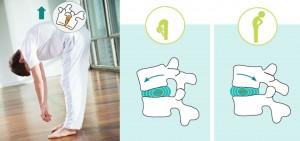
Beautifully written
Thank you Laura!
Thank you for this post! It is very valuable to me not only as a teacher but also as a student, practitioner.