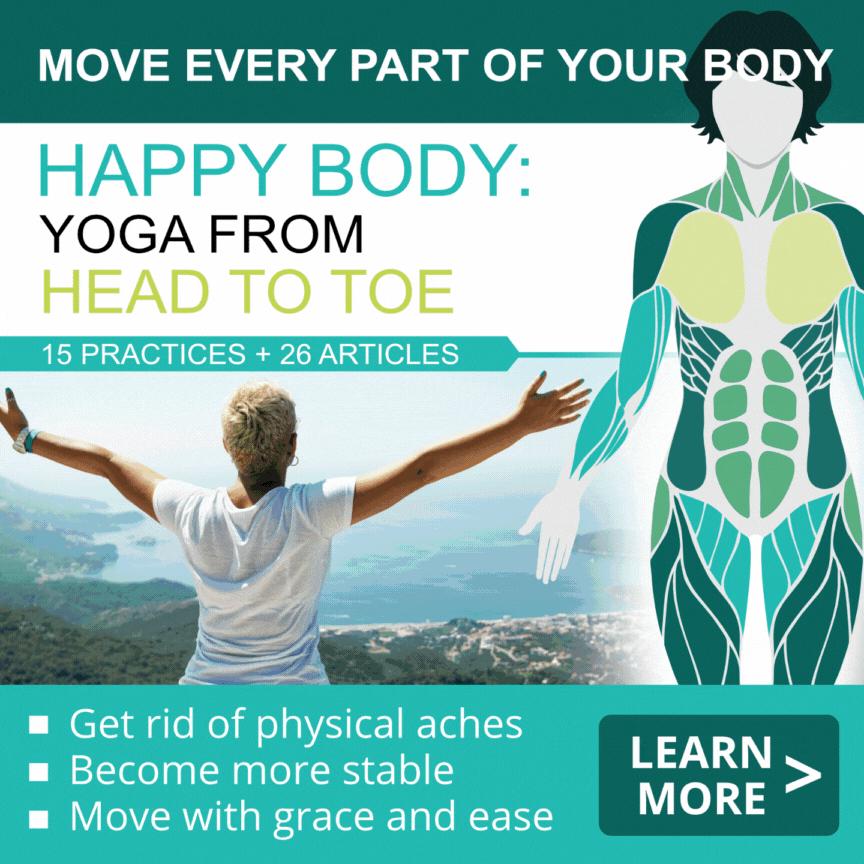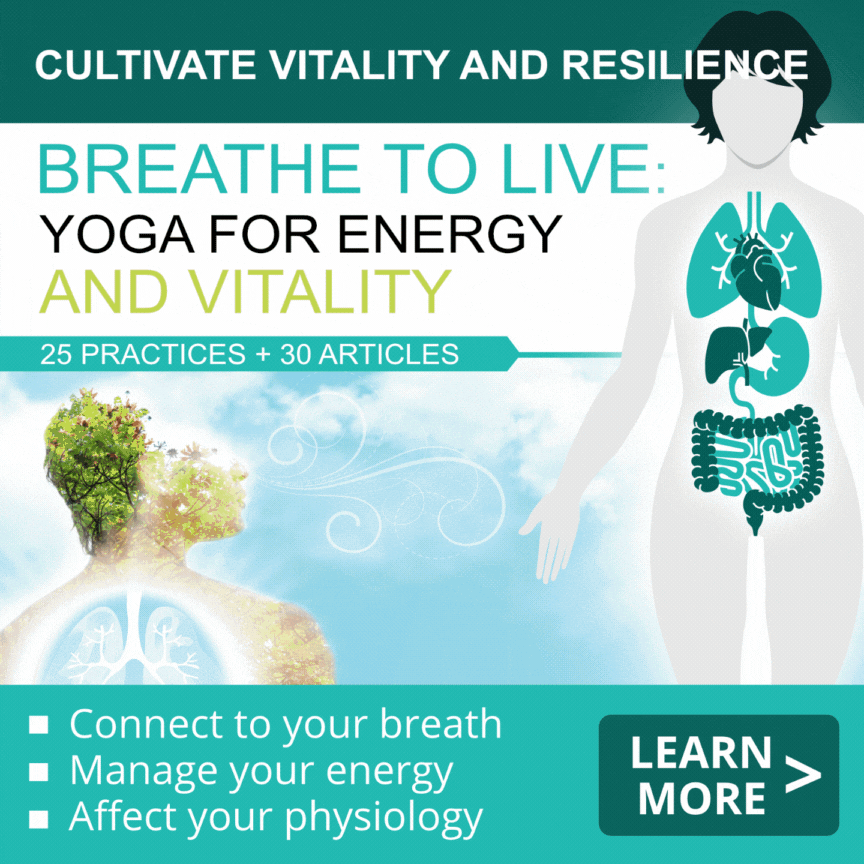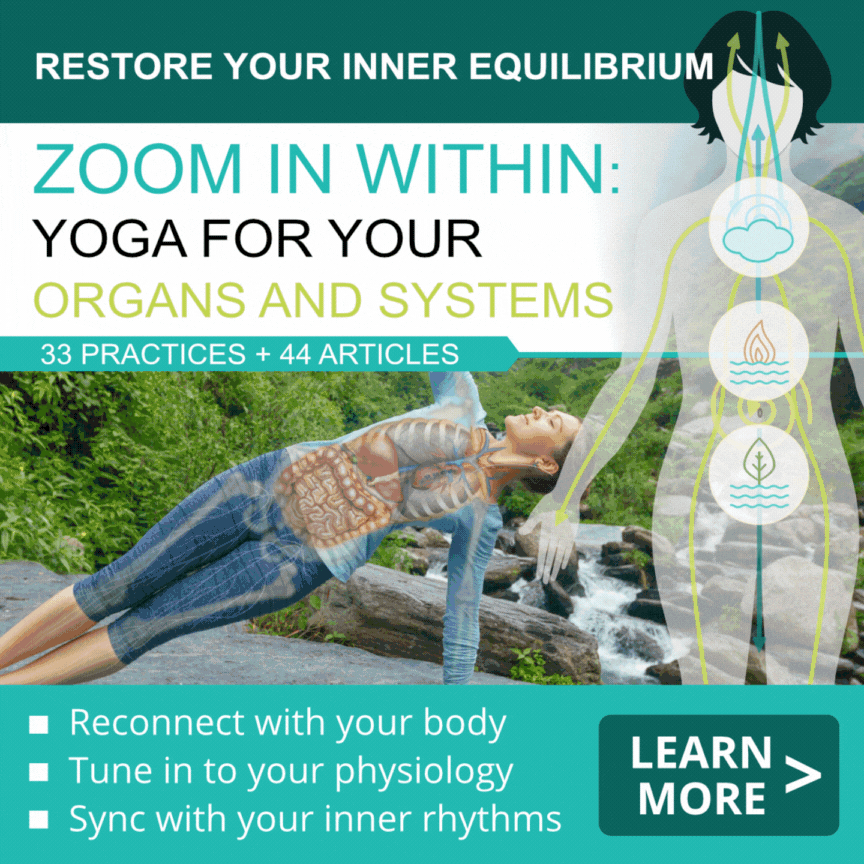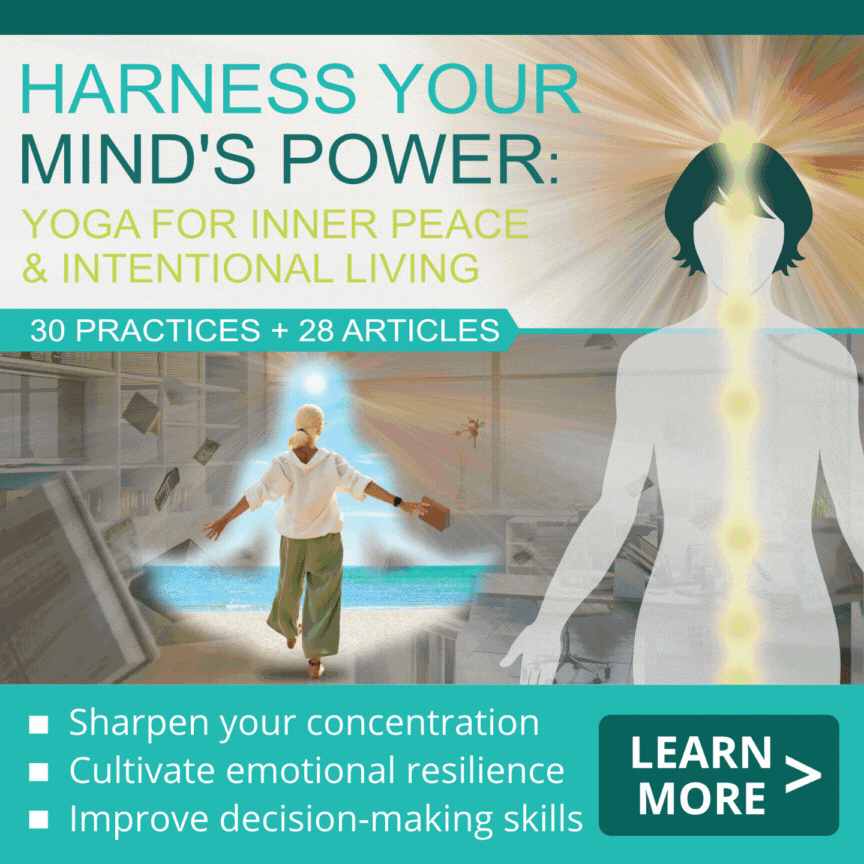
Three pillars of physiological health
7Your body likes to be in a state of internal balance. It is called homeostasis and indicates a stable internal environment. Homeostasis maintains the state of internal equilibrium on the levels of body temperature, fluid volume and composition, waste concentration and blood pressure. There is a constant juggling act going on between several physiological systems to keep your vital conditions within normal limits. You can also call it “body budget” – the body tries to balance your internal checks and balances, making sure that if there is a big expenditure of some sort, it is followed by a large deposit to replenish the resources.
Some things that you do in your daily life act as deposits toward the body budget, and some act as withdrawals. The body is sensitive about the budget going both too low and too high, while negative balances and surpluses usually lead to disease. Three most direct factors that affect the body budget on a daily basis (the pillars of physiological health) are stress, sleep and energy.
Stress is simply a fact of life; it is reflective of any change that happens within you or your environment. It has a stimulating affect on the entire system and serves as a driving force in your life. The trouble begins when you get stuck in the acceleration mode (facilitated by the sympathetic system activation) – you can drive yourself into a wall or run out of gas. In general the high-stress state is not sustainable for a long period of time because it puts incredible wear and tear on your system. That is why biology had equipped us with a handy brake system called the parasympathetic nervous system that helps regulate the drive of the sympathetic nervous system. So when it comes to stress, some stress is useful, too much stress is taxing.
Sleep is necessary for any human being to function. Some people need more sleep than others – this is highly individual. A reliable indicator of whether or not you get enough good-quality sleep is how you feel when you wake up in the morning. If you feel rested and refreshed then you are getting enough sleep; if you feel tired and/or groggy you are getting too little or too much sleep. Sleep requirements change based on the state of your body budget – if your budget is depleted you might need more sleep; if you have surplus of energy you might need less.
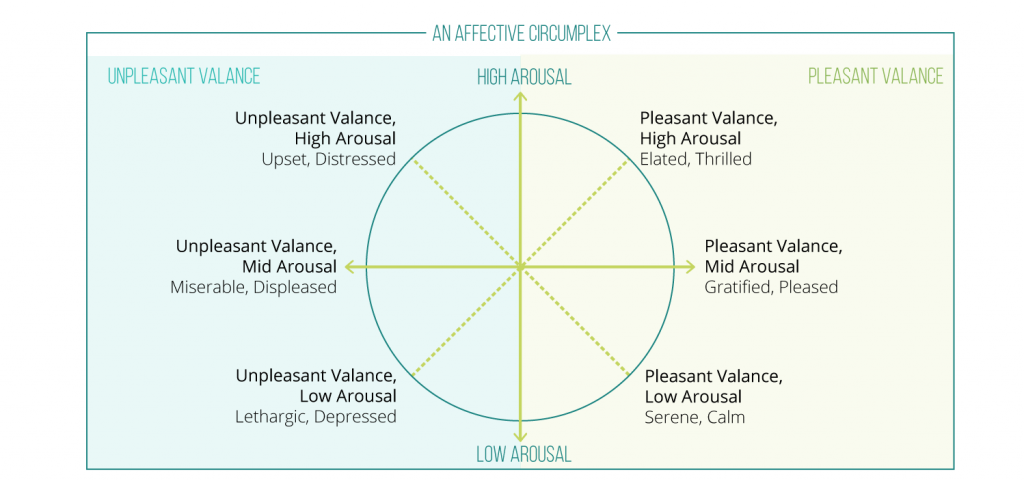
Energy is usually measured in terms of high or low arousal (a spectrum between high energy and low energy). The quality of energy is important also: high energy can manifest as being anxious and jittery, or as being alert, excited and vital; low energy can show up as lethargic and depressed, or as serene and calm. In modern science they use the term “affect” to describe the energetic state of your system moment to moment. Affect has two sides to it: valence and arousal. Valence is the general feeling of pleasantness or unpleasantness; arousal indicates how calm or agitated you feel. “Affect is the constant current throughout your life, even when you are completely still or asleep. It does not turn on and off in response to events you experience as emotional. In this sense, affect is a fundamental aspect of consciousness, like brightness and loudness.”(1)
The psychologist James A. Russell developed a useful diagram to show your affect at any given moment. “Your affect is always some combination of valence and arousal, represented by one point on the affective circumplex.”(1)
Where on this diagram are you right now? Are you tired from lack of sleep (low arousal) and enjoying a cup of warm tea (pleasant valence)? Are you energized from your morning yoga practice (high arousal) and feel ready to tackle you day (pleasant valence)?
The three pillars of physiological balance (stress, sleep and energy) are intimately linked. We all know that the level of your energy is connected to how much sleep you got and how stressed you feel. The degree of pain or discomfort that you experience will also depend on how balanced or unbalanced your body budget is. Using scientific terminology, your affect (the way you feel from moment to moment) depends on interoception (your brain’s internal perception of your body budget). “Interoception did not evolve for you to have feelings but to regulate your body budget. It helps your brain track your temperature, how much glucose you are using, whether you have any tissue damage, whether your heart is pounding, whether your muscles are stretching, and other bodily conditions all at the same time. Your affective feelings of pleasure and displeasure, and calmness and agitation, are simple summaries of your budgetary state.”(1)
This is pretty remarkable, when you think about it. It means that at any given moment you can have a pretty clear read on the state of your physiology. If you are felling generally unpleasant, your body budget is unbalanced; if you are feeling generally pleasant, your body budget is balanced. We recognize that sometimes if we acknowledge “It’s not about you, I am just feeling cranky because I didn’t get enough sleep.” Other times we blame everything and everybody for the way we feel.
So what happens if you pay enough attention to your affect to recognize when your system is out of balance? Unfortunately, “when your body budget is unbalanced, your affect doesn’t instruct you how to act in any specific way, but it prompts your brain to search for explanations.”(1) Recognizing that something is off is one thing (and a big step forward), but what do we do about it? Luckily, yoga tradition has developed a comprehensive model for managing your body budget and facilitating both deposits and withdrawals from the system (as necessary) >
 Resources
Resources
- How Emotions Are Made: The Secret Life of the Brain by Lisa Feldman Barrett
















Brilliant! Thank you. I will share with my students.
Thank you Dee!
Thank you!
I love reading your posts. Just wanted to tell you that and how appreciative the world is having your diligent passionate yoga knowledge shared. By you practicing sharing what you learnt is a true yogini. Warm blessings and love to you my dear sister. Aum.
Olga you continue to shine Light on Life. I continue to be most grateful.
Hi Olga,
Thank you for continuing to add to your site, in blogs, video and general knowledge,a
Thank you Ellen! 🙂